Introduction to Natural Medicines
In recent years, there has been a growing interest from many Australians in the potential therapeutic benefits of natural medicines. As with most emerging therapies, the evidence is limited on how effective natural medicines are at treating and managing medical conditions, which is why it’s only used when approved treatments have been tried and failed.
This article will provide a brief overview of natural medicines and the limited evidence that supports its use.
Accessing Natural Treatments & Products
The Commonwealth and State and Territory governments have allowed for the prescribing and dispensing of medicinal cannabis products. As medicinal cannabis products are not registered medicines in Australia, they can only be accessed via special pathways available for unapproved medicines. Approval from the TGA to access these medicines can only be facilitated by Australian-registered medical practitioners with appropriate qualifications and training.
Approved cannabis products come in a variety of formulations and ratios of THC/CBD. For more information on dosage formulations, click here. Below is a table of the active ingredients for cannabis products and how the different ratios (amounts) of active ingredients are categorised and scheduled.
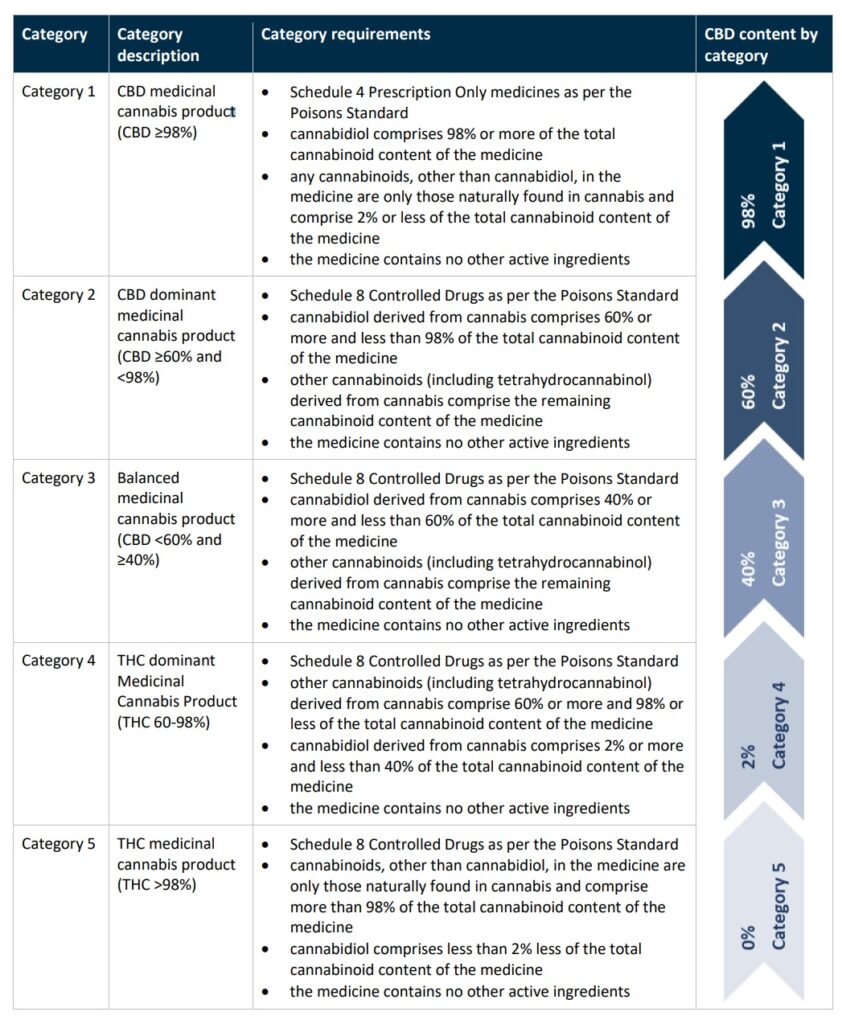
Understanding Natural Medicines
The cannabis plant is a complex plant containing many different cannabinoids and terpenes. The most well known two cannabinoids are tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD).
THC
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is responsible for the psychoactive effects of the cannabis plant. THC may also be responsible for some of the medicinal effects of cannabis such as reduction of nausea, vomiting, pain and muscle spasms as well as improvements in sleep and appetite.
CBD
A second cannabinoid, cannabidiol (CBD) is not psychoactive and may be useful in the management of seizures, pain, and may have anxiolytic and antipsychotic effects. Different cannabis strains contain different ratios of THC to CBD. It is unclear whether THC and CBD act individually or synergistically (in conjunction with each other).
Terpenes
The cannabis plant also contains terpenes, which give cannabis its flavour and aroma. It is unclear whether terpenes have their own pharmacological effects. For a deeper dive, jump over to our article on Terpenes here.
Evidence of Potential Benefits
As it currently stands, there is limited and varied evidence for the potential benefits of medicinal cannabis for the following conditions:
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Epilepsy
- Palliative Care
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Chronic Non-cancer Pain
Doctors rely on evidence to make informed decisions about the best medications for their patients. For medicinal cannabis, the amount of evidence is currently limited and the products, doses and research methods used vary between studies. This makes it difficult to come to firm conclusions about how best to use particular medicinal cannabis products.
There is also not much information available to help doctors determine the most appropriate and safe doses while minimising potential side-effects. Importantly, at the moment, relatively few studies compare the effects of medicinal cannabis products against currently approved treatments for various conditions and symptoms. In addition, most of the studies reported in the medical literature have either used purified pharmaceutical substances or smoked cannabis.
As there is limited scientific evidence to support the use of medicinal cannabis in most conditions, and in many cases the evidence is for its use together with other medicines, it should be used only when approved treatments have been tried and have failed to manage conditions and symptoms.
